 |
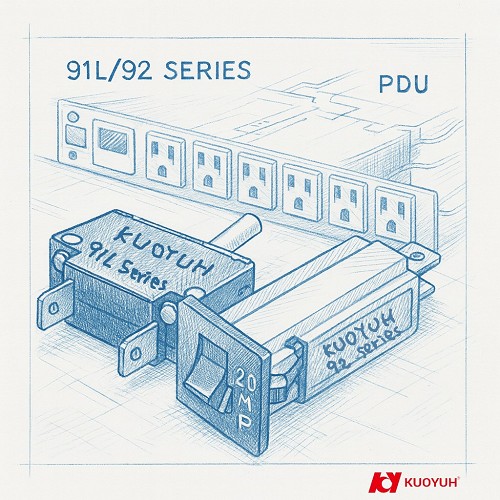
Most server rack failures do not start with the server itself; they start with the power strip. |
 |
Is your sauna heater not responding? Before you replace the entire control panel, read this technical guide. |
 |
Pool and spa systems rely heavily on consistent, stable power delivery to maintain water quality and user safety. |
 |
In solar power generation, off-grid energy storage, marine electrical systems, and RV power systems, the DC circuit breaker is the key component for electrical safety. |
 |
When traveling or living in a recreational vehicle (RV), solar power allows you to stay independent from campground electricity and continue powering essential devices such as refrigerators, lighting, charging ports, and ventilation systems. |
 |
How to Build a Safer and More Stable Trailer Power System with KUOYUH Circuit Breakers. |
 |
Combining Main and Auxiliary Protection to Safeguard HVAC Systems from Overheating and Short Circuits. |
 |
Garbage disposals have become essential in modern kitchens, efficiently grinding food scraps and preventing sink blockages. |
 |
In the safety design of electrical and electronic equipment, overload protection is essential. UL1077, the international standard for Supplementary Protectors (SPs), defines how protective devices should perform under various overload conditions. |
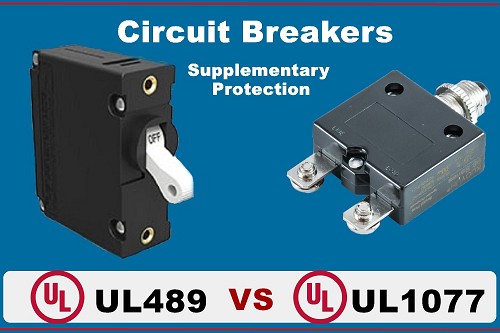 |
When it comes to electrical safety, UL standards are a global benchmark. |
 |
In modern vehicles, reliable power protection is essential for sjavascript:;afety and performance. |
 |
Picture this: you’re driving your truck down a long highway when the electrical system suddenly fails. With no spare fuses on hand, |